2026 How to Choose the Right Molded Case Breaker for Your Needs?
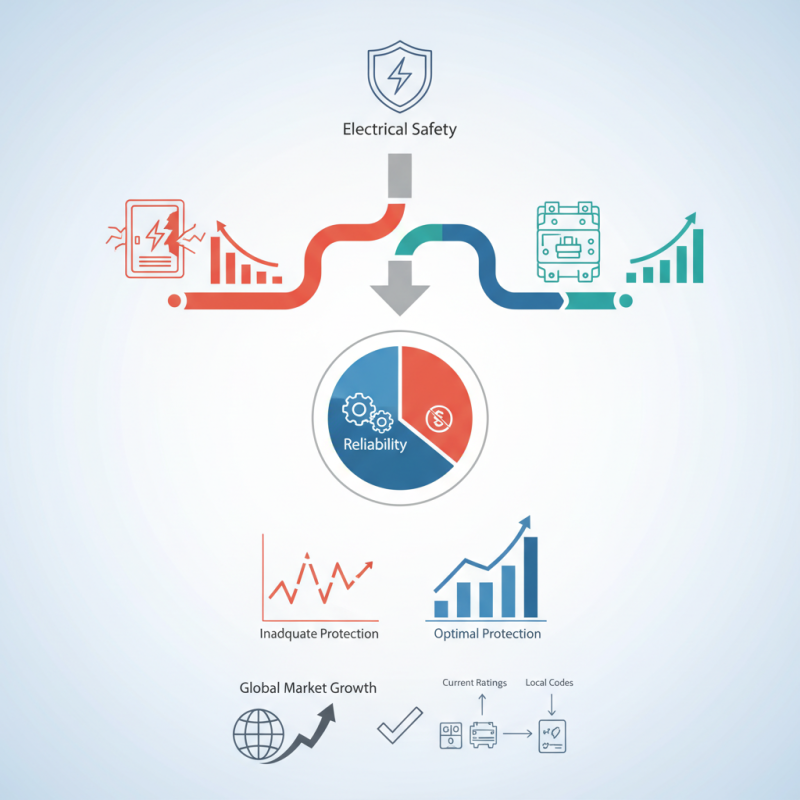
Choosing the right molded case breaker is crucial for electrical safety and efficiency. Recent industry reports indicate that over 30% of electrical failures can be traced back to inadequate protection devices. Molded case breakers serve as a key defense against overloads and short circuits, making them essential in both residential and industrial settings.
The global molded case circuit breaker market is projected to grow by 6% annually. This indicates rising demand for reliable electrical protection. Selecting the ideal breaker often involves understanding specific needs, such as current ratings and trip settings. An incorrect choice may lead to equipment malfunction or safety hazards.
While it's tempting to prioritize cost, long-term reliability should take precedence. Many users overlook the importance of adhering to local electrical codes. It's easy to assume all breakers are interchangeable, but this is a misconception that can have costly consequences. Make informed decisions to protect both people and assets.

Understanding Molded Case Circuit Breakers and Their Functions
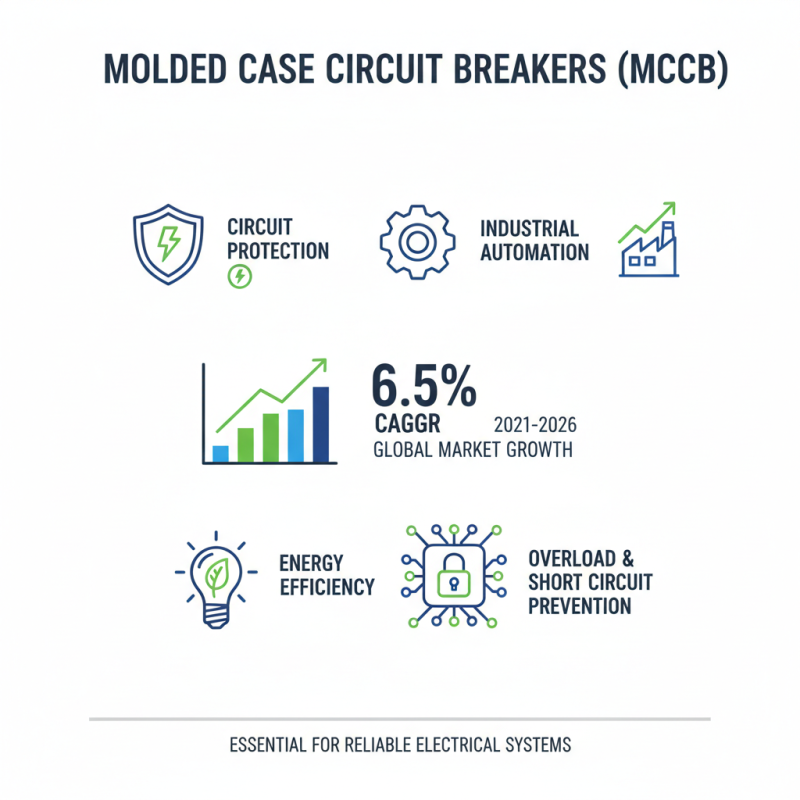
Molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) play a crucial role in electrical systems. They protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. Understanding their functions is essential for selecting the right breaker for specific needs. According to industry reports, the global MCCB market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by increasing industrial automation and the need for energy efficiency.
When considering MCCBs, assess the application requirements. Consider factors such as voltage rating, current rating, and the environment. Some MCCBs operate well in high-humidity areas, while others are better suited for dry settings. Note that not every breaker will cover all requirements. Miscalculating ratings could lead to system failures, exposing you to unexpected risks.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance is crucial for MCCB reliability. Inspect breakers periodically for signs of wear or damage.
Another critical aspect is the trip mechanism. Thermal-magnetic breakers are common. They provide protection through a combination of thermal and magnetic trips. However, there are also electronic trip units that offer advanced settings and features. Choosing the wrong trip mechanism can leave a system vulnerable.
**Tip:** Evaluate the frequency of power surges in your area. This can influence your breaker choice significantly.
Identifying Your Electrical Load Requirements for Circuit Breakers
Choosing the right molded case breaker starts with understanding your electrical load requirements. This means assessing the total amperage your circuits will require. According to recent industry studies, residential loads typically range from 100 to 200 amps. However, for commercial applications, this can exceed 400 amps, depending on the equipment and lighting used.
It’s essential to consider both continuous and peak loads. The National Electrical Code (NEC) suggests that you should start by calculating running currents. For example, if your appliances collectively draw 60 amps, add a safety margin of 25%. This brings you to 75 amps, indicating a breaker size of at least 80 amps. If you overlook peak demands, you might face frequent trips, which can be frustrating and inconvenient.
Delving into the specifics, also consider whether your loads are resistive or inductive. Inductive loads, such as motors, require breakers with higher interrupting ratings. The failure to account for this can lead to breaker damage. In reports, it’s noted that improper sizing might affect a system's efficiency by as much as 30%. Understanding these nuances is crucial in making informed decisions.
Evaluating Breaker Ratings: Amperage, Voltage, and Interrupting Capacity
When selecting a molded case breaker, understanding breaker ratings is essential. Amperage is a primary consideration. Most residential systems require breakers rated between 15 to 200 amps. For industrial use, the range can extend significantly. A report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association suggests that nearly 75% of electrical failures are linked to incorrect amperage settings on breakers. Thus, proper evaluation can ensure equipment longevity.
Voltage ratings also play a crucial role. Breakers are typically available in single-phase and three-phase options. For residential systems, 120/240V is standard. In industrial settings, three-phase systems often operate at 480V. The choice here affects performance and safety. The Voltage Ratings initiative by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers highlights that mismatched voltage ratings contribute to nearly 20% of electrical accidents.
Interrupting Capacity is another critical factor. This rating defines how much short-circuit current a breaker can safely interrupt. Many experts recommend a minimum interrupting capacity of 10kA for most applications. Failing to select the right capacity can lead to catastrophic failures. An analysis published by the Electrical Safety Foundation International showed that improper interrupting capacity settings accounted for over 30% of major electrical incidents. Understanding these ratings is crucial for safety and efficiency.
Exploring Different Types of Molded Case Breakers Available in the Market
When exploring molded case breakers (MCBs), it's essential to understand the various types available in the market. Standard MCBs are popular for general use. They protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. Another type includes those designed for specific applications. For example, adjustable MCBs allow users to set the protection level based on their needs.
Some MCBs come with integrated ground fault protection. This feature adds another layer of safety, especially in wet environments. Users often overlook this aspect. Specialty breakers are also available, like those rated for high temperatures or corrosive environments. These targeted solutions may be essential for certain industries but can come with a higher price tag.
Choosing an MCB requires careful consideration. Factors like current rating, voltage rating, and environmental conditions play a role. Do you need robust protection, or is standard adequate? The diversity in molded case breakers reflects the wide range of applications. It's not a one-size-fits-all situation. Understanding these distinctions can prevent costly mistakes. Ensure you reflect on your specific requirements before making a decision.
2026 How to Choose the Right Molded Case Breaker for Your Needs?
This chart illustrates the market share of different types of molded case breakers available in 2026. Understanding these types can help you choose the right molded case breaker for your needs.
Tips for Installation and Maintenance of Molded Case Circuit Breakers
Proper installation and maintenance of molded case circuit breakers (MCCBs) are crucial for optimal performance. According to recent industry reports, incorrect installations can lead to a 30% increase in device failure rates. Ensuring that the installation site meets necessary environmental conditions is essential. This includes controlling dust, moisture, and temperature. It's also vital to read the manufacturer's guidelines. Following these standards can minimize risks.
Regular maintenance is equally important. Routine inspections can catch issues before they escalate into significant problems. A recommended practice is to check connections monthly. Loose connections can cause overheating and device failure. In one study, 25% of circuit failures were traced back to poor connection maintenance. Cleaning dust and debris every six months can also prolong the life of MCCBs. While some may overlook these tasks, the cost of neglect can be high. Investing time in maintenance can prevent expensive downtime.
It's easy to underestimate the importance of proper usage. Many users skip precautionary checks, thinking everything is fine. However, an unserviced MCCB can lead to unexpected failures. Statistics indicate that 15% of circuit disruptions occur without warning. Evaluating the installation environment regularly can help identify potential risks before they manifest. Being proactive is far better than dealing with the aftermath.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Innovations in Molded Case Breakers at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Trends and Insights
-

Understanding the Challenges of Miniature Circuit Breakers in Modern Electrical Systems
-
2025 Top Surge Protection Circuit Breaker: Your Essential Buying Guide
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Circuit Breaker Switch
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Air Circuit Breakers for Safety?
-
Understanding Circuit Breaker Switch Types and Their Applications