9 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Home Circuit Breaker
Selecting the right home circuit breaker is vital for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your electrical system. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures are a leading cause of home fires, with improper circuit breaker suitability being a significant contributing factor. Moreover, a study by the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) reveals that nearly 51,000 electrical fires are reported in the U.S. each year, underscoring the necessity of making informed choices. As homeowners increasingly prioritize safety and energy efficiency, understanding the various types of circuit breakers—like GFCI and AFCI, along with their specifications—has become crucial. This blog presents nine essential tips to guide you in selecting the right home circuit breaker, ensuring that your home not only meets regulatory standards but also protects your family and property from potential electrical hazards.
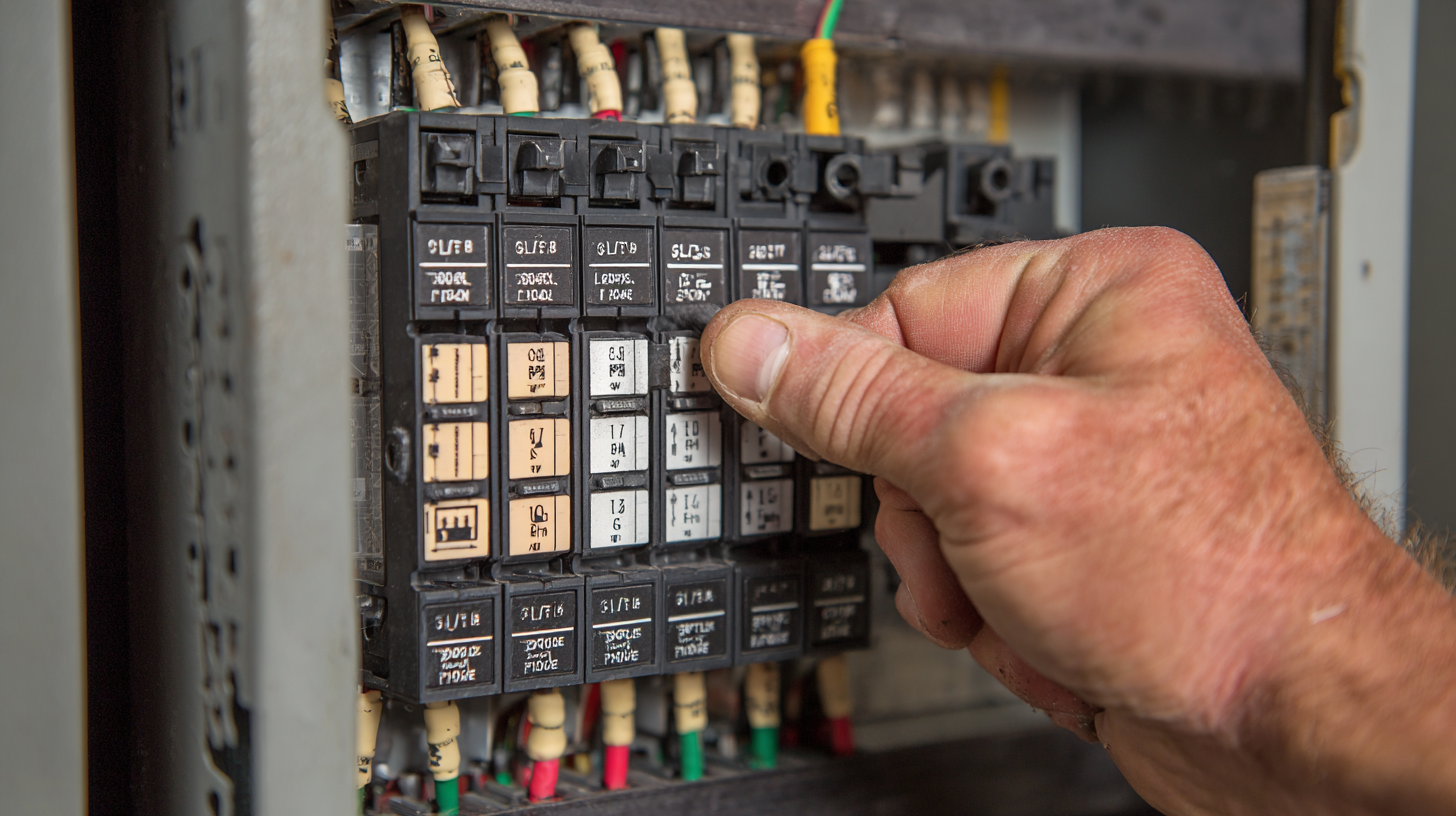
Understanding the Importance of Circuit Breaker Ratings in Home Safety
 Choosing the right circuit breaker is crucial for maintaining safety in your home. Circuit breaker ratings are essential indicators of how much current a breaker can handle before it trips. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures are a leading cause of home fires, with properties suffering an estimated annual loss of $1.3 billion due to electrical system failures. Selecting breakers with appropriate ratings can significantly mitigate these risks, ensuring that your electrical system operates within safe parameters.
Choosing the right circuit breaker is crucial for maintaining safety in your home. Circuit breaker ratings are essential indicators of how much current a breaker can handle before it trips. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures are a leading cause of home fires, with properties suffering an estimated annual loss of $1.3 billion due to electrical system failures. Selecting breakers with appropriate ratings can significantly mitigate these risks, ensuring that your electrical system operates within safe parameters.
In residential settings, most circuit breakers are rated for 15 to 20 amps, and it's vital to match these ratings to the circuits they're protecting. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) emphasizes that improperly rated breakers can lead to overheating and potentially catastrophic failures. For instance, using a 20-amp breaker on a circuit meant for 15 amps may not trip when it should, increasing the risk of electrical fires. Homeowners need to be vigilant about understanding and adhering to these critical ratings, as they are foundational to safeguarding both property and lives.
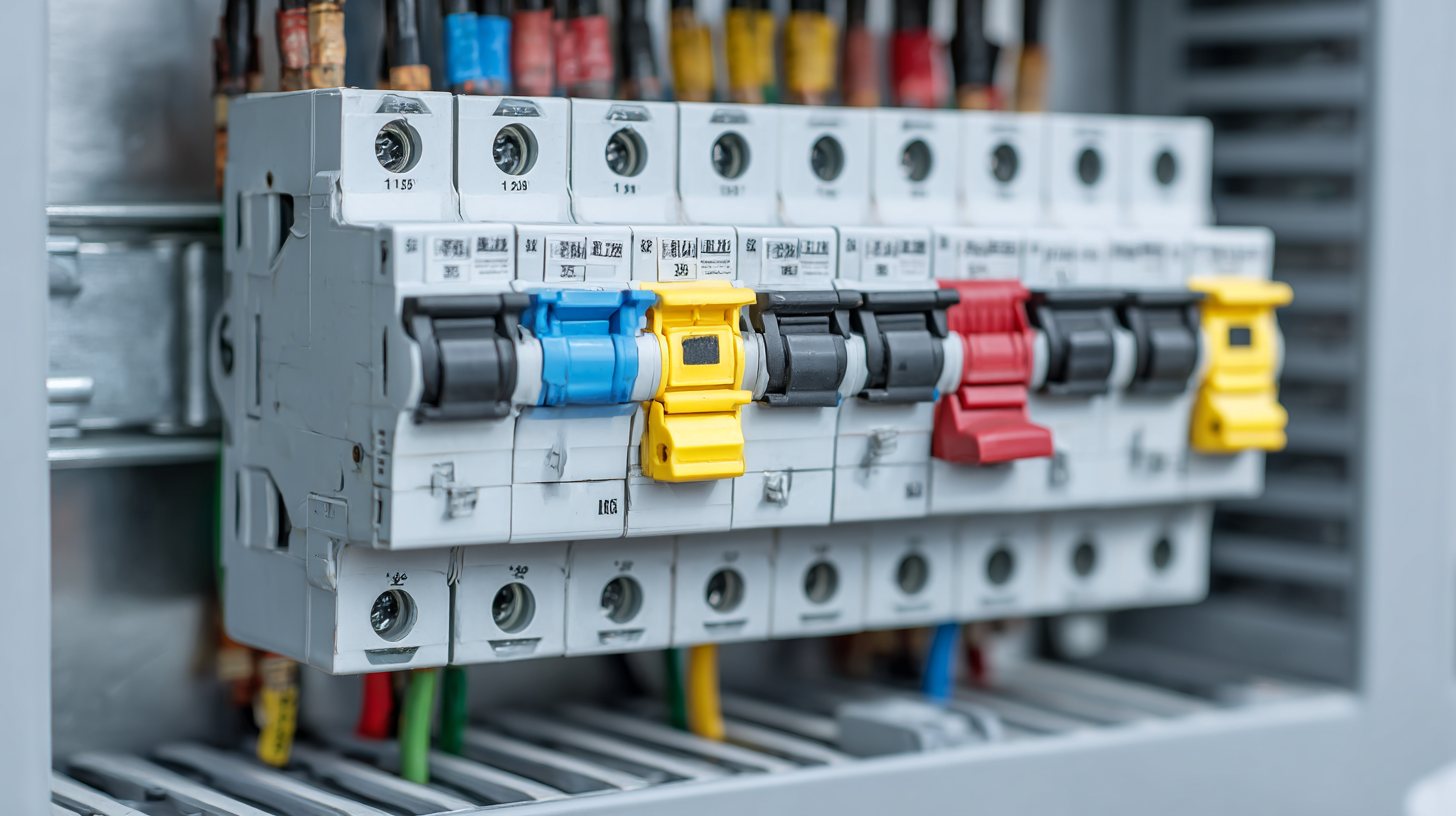
Evaluating the Types of Circuit Breakers: A Comparative Analysis for Home Use
When it comes to selecting the right circuit breaker for your home, understanding the different types available can greatly enhance your decision-making process. The most common types of circuit breakers are the standard circuit breaker, the Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI), and the Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI). Each serves a unique purpose, catering to specific safety needs within your home. Standard circuit breakers protect against overloads, while GFCIs are essential in wet areas like kitchens and bathrooms, protecting against electrical shock. On the other hand, AFCIs are designed to prevent fires caused by arcing faults in electrical wiring.
Comparative analysis of these circuit breakers reveals that choosing the right one hinges on understanding their features and applications. For instance, GFCIs offer critical protection in damp environments, making them non-negotiable for areas exposed to water. In contrast, AFCIs are increasingly required in many new constructions for added fire safety. Evaluating the specific risks present in your home and matching them with the appropriate circuit breaker type can lead to enhanced safety and peace of mind, ultimately ensuring that your electrical system is not only functional but secure.
9 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Home Circuit Breaker
| Type of Circuit Breaker | Trip Mechanism | Amp Rating | Voltage Rating | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Circuit Breaker | Electromechanical | 15-60 Amps | 120/240V | General Lighting and Outlets |
| GFCI Circuit Breaker | Ground Fault Detection | 15-20 Amps | 120V | Bathrooms, Kitchens, Outdoor |
| AFCI Circuit Breaker | Arc Detection | 15-20 Amps | 120V | Bedrooms, Living Rooms |
| Dual Function Circuit Breaker | Combination of GFCI and AFCI | 15-20 Amps | 120V | High-Risk Areas |
| Three-Phase Circuit Breaker | Thermal-Magnetic | 30-600 Amps | 480V | Commercial Applications |
The Role of Amperage: How to Choose the Right Current Rating for Your Home
When selecting the right home circuit breaker, understanding the role of amperage is crucial. Amperage, measured in amperes (amps), determines the maximum current a circuit can safely carry without tripping. According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), residential circuits typically require breakers rated between 15 to 20 amps for general use, such as lighting and standard outlets. However, high-demand appliances like air conditioning units or electric dryers often necessitate breakers rated at 30 amps or more.
One of the essential tips for choosing the right circuit breaker is to assess the electrical load of your home. Evaluating the combined amperage of all devices on a circuit ensures that you don't exceed the breaker's capacity. For instance, if you plan to power a home office with computers and equipment totaling 12 amps, a 15-amp breaker might suffice, but opting for a 20-amp breaker can provide extra headroom and prevent frequent tripping during peak usage.
Another critical aspect is considering the type of breaker you need. There are two main types: standard circuit breakers and Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs), which are necessary for areas prone to moisture, like kitchens and bathrooms. Choosing the right type of breaker not only enhances safety but also ensures optimal performance for your devices and appliances, aligning with the latest industry standards and practices.
Considering Voltage Compatibility: Ensuring Your Breaker Matches Home Electrical Needs
When choosing the right home circuit breaker, voltage compatibility is a crucial factor that cannot be overlooked. Ensuring that your circuit breaker matches your home’s electrical needs is essential for safety and efficiency. Most homes operate on standard voltages of either 120V or 240V; thus, selecting a breaker that aligns with your specific voltage requirements is fundamental. An incompatible breaker can lead to inefficient operation, nuisance tripping, or even potential fire hazards.
Additionally, determine the amperage rating that corresponds to your household circuits. Breakers are designed to protect electrical circuits by tripping when an overload of power occurs. Therefore, matching the breaker’s amperage with the load it will handle is critical. For instance, if major appliances such as ovens and dryers require 240V, choosing a double-pole breaker will ensure they operate smoothly without exceeding their load limits. Always consult an electrician if you're unsure about the specifications; their expertise can help you avoid costly mistakes and maintain a safe home environment.
Voltage Compatibility of Home Circuit Breakers
This bar chart depicts the percentage of homes using different voltage levels for circuit breakers. It highlights that the majority of homes operate on 120V, followed by 240V, with a small percentage using 480V.
Tips for Future-Proofing Your Home's Electrical System with Smart Breaker Choices
When it comes to future-proofing your home's electrical system, selecting the right circuit breaker plays a critical role. According to the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), advanced circuit breakers can enhance energy efficiency by up to 25% compared to standard models. This is particularly important as homes increasingly rely on smart devices and renewable energy sources, necessitating a robust electrical system that can handle varying loads and demand.
Additionally, the rise of smart home technology underscores the importance of integrating smart circuit breakers that offer real-time monitoring and control. A report from MarketsandMarkets indicates that the smart circuit breaker market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.4%, reflecting the increasing demand for more intelligent electrical solutions. Investing in smart breakers not only improves safety with features like overload protection but also allows homeowners to manage energy consumption more effectively, paving the way for a sustainable future. Choosing breakers that are compatible with smart home systems not only prepares your home for current technology but also builds resilience against future advancements.

Related Posts
-

Understanding the Challenges of Miniature Circuit Breakers in Modern Electrical Systems
-

Innovative Usage Scenarios of DC Molded Case Circuit Breakers in Modern Electrical Systems
-

Understanding the Key Differences Between Types of Vacuum Circuit Breaker Technologies
-

10 Essential Tips for Surge Protection: Protect Your Electronics with 99% Effectiveness!
-

What is the Function of a DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
-

How to Choose the Right Motor Protection Relay for Your Application