Best Power Distribution Solutions for Efficient Energy Management?
In today's energy landscape, efficient power distribution is essential for sustainability and reliability. Experts emphasize the importance of innovative solutions. John Smith, a renowned figure in the power distribution industry, states, "Effective power distribution systems can transform how we manage energy." His insights highlight the growing need for advanced management techniques.
Power distribution networks are the backbone of modern energy systems. However, many existing infrastructures struggle with inefficiencies. Issues like energy loss and outdated technology can hinder progress. We must examine the current state of power distribution to identify areas for improvement.
Moreover, integrating smart technologies can lead to better energy management. These solutions can optimize energy flow and reduce waste. While advancements exist, there are still challenges to overcome. Addressing these flaws is crucial for the future of power distribution. By focusing on innovative approaches, we can create a more efficient energy landscape.

Best Practices for Power Distribution System Design in Energy Management
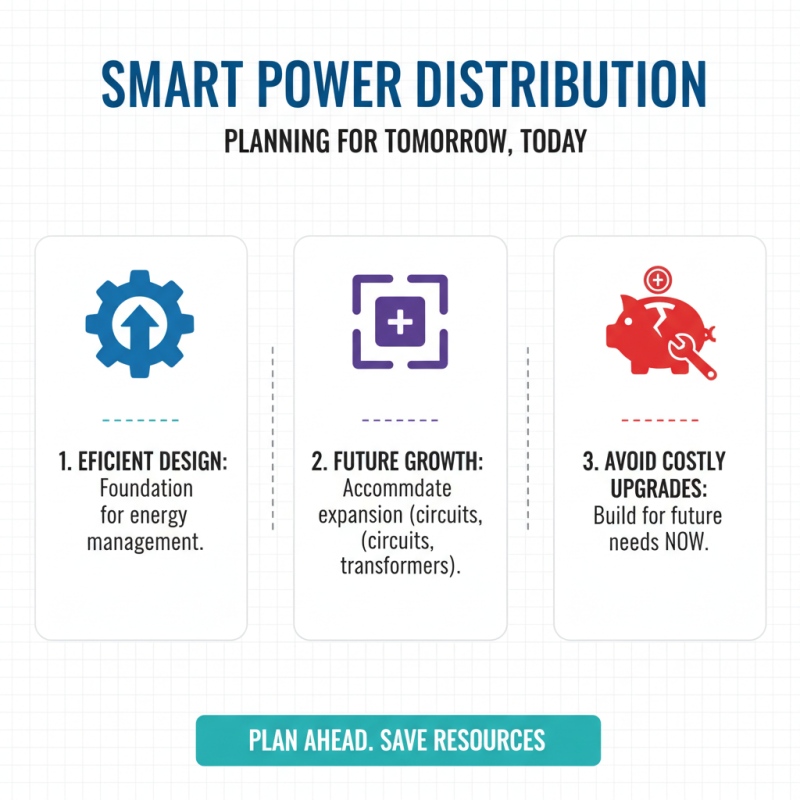
Efficient energy management begins with a well-designed power distribution system. The layout should accommodate future growth, which is often overlooked. Space for additional circuits or transformers is essential, yet many systems are built for current needs only. This can lead to costly upgrades later.
When designing a power distribution system, consider load balancing. Uneven loads can cause overheating and reduce system lifespan. Ensure circuits are adequately utilized to prevent waste. It's crucial to regularly review load data and adjust configurations as necessary. Small changes can lead to significant improvements in efficiency.
**Tip:** Always include spare capacity in your design. It’s better to have it and not need it than to need it and not have it.
Another critical aspect is integrating technology. Smart meters and monitoring systems can provide real-time data. This data helps manage energy consumption effectively. However, implementing technology can be daunting. Training staff and ensuring compatibility with existing systems are common challenges.
**Tip:** Begin with pilot projects to test new technology before full-scale implementation.
Analysis of Smart Grid Technology Impact on Power Distribution Efficiency
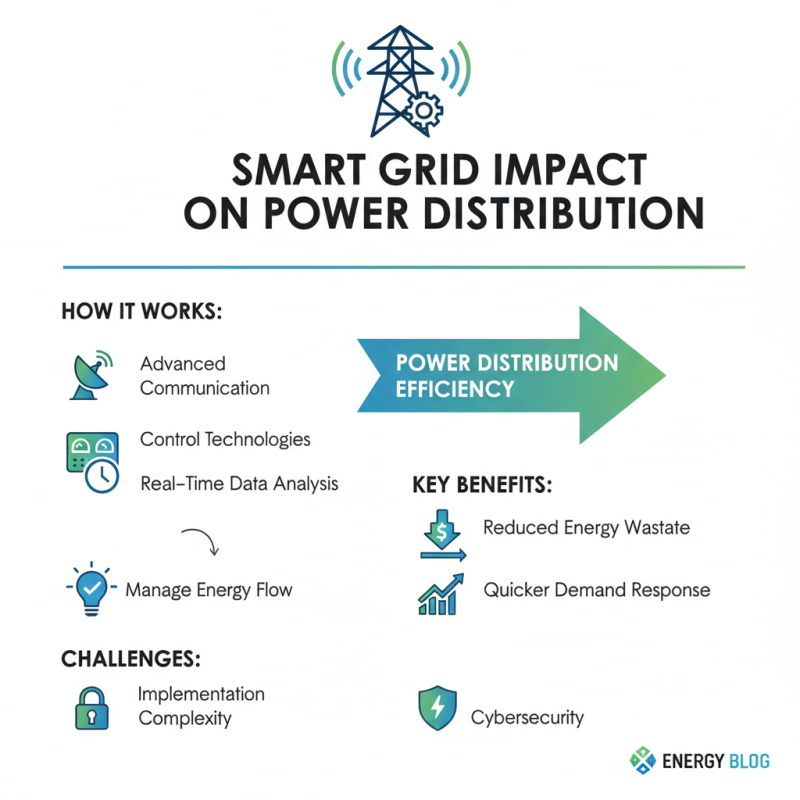
The integration of smart grid technology significantly impacts power distribution efficiency. Smart grids use advanced communication and control technologies to manage energy flow. This system allows for real-time data analysis, enabling utilities to respond quickly to changes in demand. As a result, energy wastage is reduced. However, implementing this technology presents challenges.
One key issue is the need for upgrading existing infrastructure. Many power distribution systems are outdated and may not support new technologies. Additionally, cybersecurity becomes a major concern, as more connected devices increase the risk of attacks. Training for personnel is essential. Without proper education, the workforce may struggle to adapt to these changes.
Moreover, smart grids rely heavily on user participation. Consumers must engage with dynamic pricing models and energy-efficient practices. This engagement can be difficult. Some may resist changes due to a lack of understanding. Education and incentives could help bridge this gap. A collective effort is necessary to ensure that smart grids fully realize their potential.
Comparative Review of Renewable Energy Integration in Distribution Systems
The integration of renewable energy in distribution systems is gaining momentum. Recent reports indicate that renewables accounted for 29% of global electricity generation in 2023. Solar and wind power are leading this charge. However, challenges remain in effectively managing this integration. The variability of renewable sources can strain existing distribution networks.
Efficiency is key. A study found that effective integration reduces energy losses by up to 15%. Smart grid technologies play a vital role. These technologies enhance real-time monitoring, leading to better balance in supply and demand. Yet, many regions still lack the necessary infrastructure. This gap creates inefficiencies and hinders progress.
Not all solutions work perfectly. Some regions face regulatory hurdles. These can slow down the adoption of renewable energy systems. Additionally, battery storage solutions, while promising, are costly and still evolving. A report highlighted that only 14% of utilities have embraced large-scale battery storage. Improved strategies and investments are essential to overcome these barriers.
Evaluation of Demand Response Strategies in Power Distribution Networks
In modern power distribution networks, demand response strategies play a crucial role. These strategies aim to balance energy loads during peak times. They involve encouraging consumers to adjust their energy use. The incentives provided can range from price reductions to reliability rewards.
Implementing these strategies can be challenging. Some consumers may resist changing their behaviors. Others might not have the necessary flexibility in their routines. For instance, businesses relying on continuous operations could find it hard to reduce consumption. This necessitates a closer examination of consumer habits and preferences.
Effective demand response requires robust communication systems. Utilities must inform customers about peak times and possible savings. However, not all communication methods reach everyone equally. Some technology gaps could leave certain demographics uninformed. This gap can lead to inequalities in participation. Ultimately, the success of demand response hinges on addressing these challenges. It’s important to engage communities effectively and adjust strategies accordingly. Balancing technological needs with human behavior remains a complex task.
Key Metrics for Measuring the Efficiency of Energy Distribution Solutions
Efficient energy distribution plays a crucial role in sustainable energy management. To measure how well an energy distribution system performs, several key metrics should be considered. One important metric is the Energy Loss Ratio. This ratio reveals how much energy is wasted during distribution. A lower ratio indicates better efficiency.
Another metric is Load Balance. It assesses how evenly energy demand is distributed across the network. Imbalances can lead to equipment stress and increased operational costs. A well-balanced load enhances reliability and efficiency.
Tips: Identify areas where energy loss occurs. Regular audits can reveal hidden inefficiencies. Optimize load distribution using smart technologies. Monitor energy patterns frequently; changes indicate opportunities for improvement.
Additionally, consider operational uptime. High availability reduces interruptions and enhances productivity. It is essential to continuously review operational protocols. This reflection may uncover outdated practices that hinder progress. Making adjustments can lead to significant efficiency gains.
Best Power Distribution Solutions for Efficient Energy Management
This chart represents the efficiency measurements of various power distribution solutions based on key metrics such as energy loss, operational cost, and reliability score. The data illustrates the comparative performance across these metrics.
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Power Distribution Systems for Enhanced Efficiency and Safety
-

How to Optimize Power Distribution Systems for Maximum Efficiency
-
Understanding Power Circuit Breakers: The Key to Safe Electrical Systems
-

2025 Top Switch Disconnector Trends and Key Features You Need to Know
-
What is a Power Circuit Breaker and How Does It Work in Electrical Systems
-
2026 How to Choose the Best Circuit Protection Solutions for Your Devices?